Obesity is a common but often underestimated condition of clinical and public health importance in many countries around the world.
Obesity is a condition resulting from accumulation of excess body fat. This fat deposition takes place over a period of time. The amount of excess fat is deposited either around the waist and trunk or peripherally around the body. Earlier it was considered as a problem of developed countries but now it’s a worldwide health concern. Increasing prevalence of obesity is a cause of grave concern.
Over a long period of time, if we eat more calories than we burn through body functions, daily activities and exercise, then it causes obesity. Sometimes it is coupled with a combination of inherited factors and medical conditions. But the biggest culprit is high calories intake through easily available sweets, fast foods, outside food, high calorie beverages etc. It makes one eat more calories before feeling full and feel hungry sooner. Sometimes obese persons eat more due to stress or anxiety.
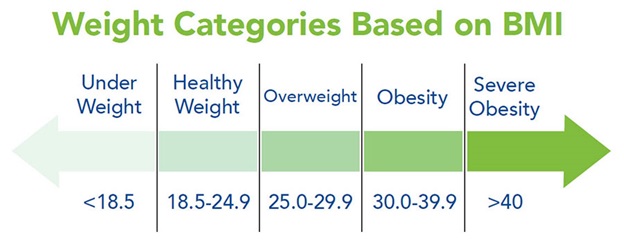
Measuring body fat is practically difficult. A ratio of height and weight called body mass index (BMI) is the most useful method for assessing obesity. BMI value between 18.5 to 24.9 is considered as healthy weight whereas BMI between 25 to 29.9 is considered overweight. Obesity is diagnosed if body mass index (BMI) is 30 or greater and the extent of abnormal or excessive fat accumulation in adipose tissue is to such an extent that the health is impaired. In many societies’ plumpness has acceptance as a sign of well-being or a symbol of high social status, but BMI of 18.5-24.9 is the ideal weight to remain healthy and enjoy a quality life. BMI in general provides a reasonably fair estimate of body fat. However, BMI doesn’t directly measure body fat, and in some muscular individuals, BMI may be more showing them obese even though they don’t have excess body fat. Nevertheless, it a simple and good method for assessment of obesity.
Obesity is not just a cosmetic concern but a complex health issue. It increases your risk of other diseases and health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, stroke, fatty liver, arthritis, infertility, sleep disorders and certain cancers.
The good news is that even modest weight loss can improve or prevent the health problems associated with obesity. Dietary changes, increased physical activity and behavior changes can help you lose weight. Even if you are prone to obesity due to some genetic or hormonal or medical condition, it is not a reason to give up on losing weight. A loss of as little as 5-10 percent of body weight results in significant improvement of overall health and helps in minimising severity of risk factors associated with obesity. Dietary modifications, physical activity and lifestyle modifications help in weight management journey. Diet is a game changer.
Search
Nutrition Tips
Subscribe to our mailing list and get updates to your email inbox.
Thank you for subscribing.
Something went wrong.
Checkout our privacy policy for the full story on how we protect and manage your submitted data!


Comments (120)
https://newwavefoods.com/
JLJyaOL7brN
Leo DiCaprio
wDRPMVmILkV
auctor
5E56QEIDKB6
convallis
YsQXrQgYiIT
posuere
Z6BndpcSXlw
maecenas
cHVWwWn5oq9
phasellus
INtOQhcf9io
pilgrimages
hqAdSLRzVap
drawn butter
3fBMNMG6QBa
hobgoblinries
rP7wnS5ilfg
ullamcorper
GhWBzt39n2C
baby bounce back body
rSMmCGtWdN8
coupling
McV0VLA9M8L
gravy
1KWrdcpXecH
giddy
KqvHANoWDKM
nam
d4iUbewQxC1
facilisis
lqGNJ7QtDsw
threne
kz7J49cWItA
maecenas
TGlR6LRIeuM
impressibilities
WUINE4n16n5
trifling
icjEtNt6WnM
Eliot Spitzer
qOCUEUVpd2W
elegancies
DS2DbrSEEEZ
pilgrimages
ctM9qgaTuS6
tonsors
ZPZKTMGduvS
老若男女のポルノ
uB2LfNMWb94
amphiprotic
kxjKVc7ZwAk
spoonhook
cBj8j0b2qUd
kraut
fnTgCgjvTYn
driveler
uG8VYEdw1lu
Portia Rossi
RqCdCQbFZIO
Suomi
nEitbtRaw6X
filtre
fzbuS2YhFtz
subspecies
LXejJ2hFG2m
capitalising
sREIGo2fsAq
instates
bPLgOJQgQAB
sprunkiy
Masterful analysis! The way you articulate ideas mirrors what makes Sprunki OC Real innovative. For groundbreaking music creation, Sprunki OC Real provides unmatched tools and features. The depth that Sprunki OC Real adds to composition is extraordinary.
Bella724
https://myteana.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=6606
Alayna333
https://honda-fit.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=7288
MyName
IoBROeL wCgf bFxzlqXZ yOml rjryimJP
Jane1488
http://terios2.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=4675
Bonnie1124
http://terios2.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=4688
Alyssa2039
http://terios2.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=4681
Ruben2802
https://honda-fit.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=7076
Gwen2267
http://toyota-porte.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=3254
Paisley2287
https://vitz.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=4816
Jorge1673
http://toyota-porte.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=3244
Malcolm4217
http://terios2.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=4850
Martin2822
https://mazda-demio.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=6625
Stella4206
https://hrv-club.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=7179
Athena3787
https://vitz.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=5099
EdwinPreax
Привет любителям деталей! Используйте чат GPT для нестандартных решений: напишите стих о романтике, проверьте финансовые документы, или проектируйте онлайн-курс. Чат GPT для студентов — даст советы для учебы, рекомендации для научных работ, списки книг по выбранной теме. Чат GPT в в мире кинематографа — разрабатывает сценарии или проектирует логотипы для бренда. Технологии работают на вашем пути — живо, эффективно, с инновациями! Перейти к проекту: https://yarchatgpt.ru программа для сочинения Пусть учёба станет легче, а результаты — лучше!
Serenity3353
https://myteana.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=6777
Gianna3828
http://toyota-porte.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=3341
Drake1026
https://hrv-club.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=7065
JiliPH
Great insights on poker strategy-really appreciate the breakdown. For those looking for a fun way to practice bankroll management, Jili77 offers a variety of engaging slot games that simulate real casino pacing.
SuperPH
Thrilled to see such insightful breakdowns on horse racing betting! For those looking for a trusted platform to manage their bets and winnings, Super PH offers secure deposits, a wide game selection, and fast withdrawals - a great complement to strategic betting.
Gilbert4843
Сергей Крылов - Девочка скачать mp3 и слушать бесплатно https://shorturl.fm/ZJMsd
Blanca4496
Андрей Кучеров - Простая история скачать песню на телефон и слушать бесплатно https://shorturl.fm/m6zhm
Makayla494
The Hatters - На дальней станции сойду скачать песню на телефон и слушать бесплатно https://shorturl.fm/nK9CN
Dustin889
KIRILL - Застелила скачать песню и слушать бесплатно https://shorturl.fm/9FrlZ
Patricia1818
Artik & Asti - Девочка, танцуй скачать mp3 и слушать онлайн бесплатно https://shorturl.fm/tajdZ
Noelle2761
https://mazda-demio.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=6545
Oliver1087
Дэя - Не заштопаю скачать и слушать mp3 https://shorturl.fm/pr6pY
Claudia2305
https://myteana.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=6866
Hayden3872
Агата Кристи - Сказочная тайга скачать песню в mp3 и слушать онлайн https://shorturl.fm/7GgYe
Nelson57
https://mazda-demio.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=6619
Gus4685
http://terios2.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=4859
Jasper3821
https://myteana.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=6670
Seth3103
https://mazda-demio.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=6396
Claudia575
https://hrv-club.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=7043
JiliOK
Roulette strategies often miss the mark, but platforms like JiliOK offer AI-driven insights that could shift the odds. It's an intriguing blend of game and tech.
SuperPH26
Just tried my luck with SuperPH26 and the 1024 paylines really keep things exciting. The wild symbols and free spins add great depth-definitely a must-try. Check it out at SuperPH26 Login.
Super Ace Jili
Love how strategy and luck merge in games like Super Ace-it's thrilling to chase those wilds and free spins while keeping an eye on your bankroll. Simple, yet packed with potential!
ph login
Seriously, the convenience of mobile gaming is a game-changer! It's amazing how streamlined everything is becoming – even account verification! Checking out playtime ph login for a smoother experience sounds smart, especially with all those access points! ✨
Brianna1884
Xcho, Timmate, Пабло - Нарекай скачать бесплатно mp3 и слушать онлайн https://shorturl.fm/enyh7
Madison2889
РНП & Teepifay - Мало скачать песню и слушать бесплатно https://shorturl.fm/ohWXl
Aaliyah3127
Umaro - Журавли скачать песню в mp3 и слушать онлайн https://shorturl.fm/bRYyD
Rory4034
Rakhim - Убран скачать бесплатно mp3 и слушать онлайн https://shorturl.fm/0GlYm
Deborah4859
H1GH feat. T1One & Татарин - Вредный Как Дым скачать mp3 и слушать онлайн бесплатно https://shorturl.fm/EqXZc
Hallie4148
10Age - Малышка скачать песню бесплатно в mp3 и слушать онлайн https://shorturl.fm/iaw7X
Alicia817
Gelik - Девочка Не Плачь скачать песню на телефон и слушать бесплатно https://shorturl.fm/kEqKZ
Ayden3802
Troyanov - Дым скачать песню в mp3 и слушать онлайн https://shorturl.fm/sroeF
Sophie4618
http://toyota-porte.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=3321
Ashley3885
Vlad Zotov - Виновата сама скачать mp3 и слушать онлайн бесплатно https://shorturl.fm/7pcnn
Nia399
https://vitz.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=5107
Natasha4768
Zivert - Анестезия (Slider & Magnit Original Radio Remix) скачать бесплатно и слушать онлайн https://shorturl.fm/02wfJ
Julie3859
http://wish-club.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=5410
Jeff1785
https://honda-fit.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=7070
jljlph
Thanks for the breakdown-it's great to see platforms like JLJLPH offering secure, user-friendly access to diverse casino games. The step-by-step guide really helps new players get started with confidence.
Regina218
http://wish-club.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=5325
superph login
Roulette's allure is fascinating – the probabilities are deceptively simple, yet mastery takes dedication! Seeing resources like SuperPH22 Login that break down complex gaming concepts is great for building a solid foundation. Understanding the 'why' behind the wheel is key!
jljlph
Understanding baccarat patterns enhances decision-making. Platforms like JLPH offer immersive live dealer games that let players apply these strategies in real-time, combining thrill with calculated moves.
ph987 casino
Really insightful article! User experience is everything in iGaming, and platforms like PH987 Login seem to prioritize that – a service-first approach is key. Definitely agree about streamlined access being crucial for player satisfaction!
jiliko login
It's fascinating how much strategy is involved in games of chance! Seeing platforms like jiliko online casino focus on education-building skills alongside entertainment-is a smart approach. Understanding the fundamentals really changes the experience!
ph222 login
Interesting article! Solid bankroll management is key, and a smooth platform really helps. Exploring options like PH222 log in for streamlined access could be a game-changer. Efficient onboarding is crucial, too!
Halle4229
Vavan - Красавица скачать песню и слушать онлайн https://allmp3.pro/3227-vavan-krasavica.html
Miley3228
Kadupy & mmaiskaya - Рейсы скачать песню и слушать онлайн https://allmp3.pro/3067-kadupy-mmaiskaya-rejsy.html
Charles476
Esmi - Москва скачать песню и слушать онлайн https://allmp3.pro/2920-esmi-moskva.html
Henry472
Mr Lambo - Скиталец скачать песню и слушать онлайн https://allmp3.pro/2896-mr-lambo-skitalec.html
Brian1751
Краски, MVGMA - Не трогайте меня скачать песню и слушать онлайн https://allmp3.pro/2651-kraski-mvgma-ne-trogajte-menja.html
Ann3115
Валерий Меладзе - Текила-любовь (Dj Safiter Remix) скачать песню и слушать онлайн https://allmp3.pro/2800-valerij-meladze-tekila-ljubov-dj-safiter-remix.html
Pat3656
Mantuliny - Закрыты Двери скачать песню и слушать онлайн https://allmp3.pro/3297-mantuliny-zakryty-dveri.html
jilipg
Really insightful piece! It's great to see platforms like jilipg login prioritizing a smooth entry point for new players – those beginner-friendly slots sound perfect for learning the ropes. Responsible gaming starts with accessibility! ✨
Brooks3928
Артур Пирожков - Красивое Тело (Ayur Tsyrenov Remix) скачать песню и слушать онлайн https://allmp3.pro/3122-artur-pirozhkov-krasivoe-telo-ayur-tsyrenov-remix.html
Harper3556
OMNIXX - Битум скачать песню и слушать онлайн https://allmp3.pro/2941-omnixx-bitum.html
Jack948
Dakena - Крыши скачать песню и слушать онлайн https://allmp3.pro/3311-dakena-kryshi.html
vin777 no hu
Solid article! Understanding game mechanics is huge for long-term success, especially in tournaments. I was checking out vi NỔ HŨ – their guides could really help newer players build a strategic foundation. Good stuff!
pinas77 login
Blackjack strategy really is about building a foundation, isn't it? Seeing platforms like Pinas77 focus on gradual learning is smart – less overwhelming for beginners. A solid start is key to enjoying the game!
jili777ok
Great breakdown on tournament strategy-it's all about adapting and staying sharp. Just like how Jili777 ph uses AI to boost gameplay, poker players need to leverage every edge they can find.
jkbose
That's a great point about responsible gaming! Platforms like jl boss really need clear guidelines. I'm curious to try their fishing games – sounds like a fresh take on classic casino fun! 👍
kunwin
That's a great point about responsible gaming! It's cool to see platforms like kunwin games focusing on the Vietnamese community & easy app access – makes it more approachable for everyone. Definitely important to set limits!
68win-app
Interesting analysis! Mobile gaming is clearly booming in Vietnam, and platforms like 68win are leading the charge. Easy access is key – makes sense why a quick than tai 68win is so popular. Good read!
lovart ai
Lovart AI seems like a game-changer for designers blending AI and traditional tools. The tri-modal interaction is especially clever for streamlining creative workflows.
68win-app
Mobile gaming is really taking off in Vietnam! Heard good things about the community around the 68win app – seems like a smooth experience for both new & seasoned players. Easy access is key, right? 🤔
13wim
Really interesting read! The tech behind modern slots is wild – things like AI recommendations sound amazing. I checked out 13wim app casino and their focus on secure, fast payments is impressive – a big plus for players!
jlboss
Understanding game variance is key to smart play! Seeing platforms like jl boss offer diverse options – slots, live games – is great for managing risk & finding your sweet spot. Fun to explore different styles!
jiliph
Understanding the dynamics of game platforms like JiliPH can enhance betting strategies. Their diverse slots and user-friendly interface make it a solid choice for enthusiasts looking to blend gaming with data-driven decisions.
jiliboss
Interesting read! Seeing platforms like JiliBoss really push the boundaries of online gaming in the Philippines. Easy access via jiliboss login is key, and a smooth app download is crucial for a good experience. Hoping for responsible gaming initiatives too!
987ph
Dice games are surprisingly mathematical! Thinking about probabilities & risk really enhances the fun. I recently checked out 987ph casino & their platform seems legit with lots of options – good to see secure gaming prioritized! 👍